While various treatment options exist, including medical procedures, vitamins for varicose veins offer a natural and accessible way to support vein health and potentially improve their appearance.
Varicose veins, those twisted, bulging veins that often appear on the legs, can be more than just a cosmetic concern. They can sometimes signal underlying issues with vein health and circulation.
Table of Contents
Understanding Varicose Veins
Before we delve into the benefits of vitamins for varicose veins, let’s understand what causes these unsightly veins.
Veins have one-way valves that keep blood flowing towards the heart. When these valves weaken, blood can flow backward and pool in the veins, causing them to stretch and bulge. This leads to the formation of varicose veins.
Key Vitamins for Varicose Vein Support
Several vitamins play a crucial role in maintaining healthy veins and circulation:
1. B Vitamins: Essential for Circulation and Vein Health
B vitamins are crucial for cardiovascular health and can offer significant benefits for varicose veins.
- Niacin (Vitamin B3): Niacin helps lower cholesterol levels and improve circulation, reducing the strain on veins and supporting healthy valve function [1]. It also has anti-inflammatory effects and can increase nitric oxide production, which helps relax blood vessels.
- Vitamins B6 and B12: These B vitamins work similarly to vitamin E by reducing blood clotting tendencies. They help regulate homocysteine levels, an amino acid that can contribute to blood vessel hardening, inflammation, and oxidative stress [2]. By keeping homocysteine in check, B6 and B12 help maintain healthy blood flow and reduce stress on the veins.
2. Vitamin E: Protecting and Strengthening Veins
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agent that offers protection and support for your veins [3].
- Improved Circulation: Vitamin E helps improve blood flow and overall vein health. It also prevents platelets from sticking to the lining of blood vessels, reducing the risk of blood clots.
- Reduced Blood Clot Risk: A study showed that a daily dose of 600 IU of vitamin E reduced the occurrence of blood clots by 21% [4]. Blood clots can further damage veins and contribute to varicose veins.
Vitamin E pairs very well with fish oil, which will also assist with blood flow via anti-inflammatory effects.
3. Vitamin C: Boosting Collagen and Circulation
Vitamin C, renowned for its antioxidant properties, also plays a vital role in vein health.
- Collagen Production: Vitamin C is essential for collagen synthesis, which helps strengthen vein walls.
- Elastin Production: Vitamin C is also needed to produce elastin, a protein that keeps veins flexible and elastic.
- Nitric Oxide Production: Vitamin C helps increase nitric oxide levels, which dilates blood vessels and improves circulation [5].
Studies have linked vitamin C deficiency to an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Adequate vitamin C intake can help support healthy veins and circulation.
4. Vitamin K: Essential for Blood Clotting and Vein Integrity
While it might seem counterintuitive to use a vitamin that promotes blood clotting for varicose veins, vitamin K is actually crucial for maintaining healthy veins.
- Coagulation: Vitamin K is essential for blood clotting, which is necessary to stop bleeding and repair damaged blood vessels.
- Vein Wall Support: Vitamin K also helps strengthen blood vessel walls, particularly in the capillaries, which are often affected by varicose veins [6].
Comprehensive blends like bone & heart minerals for vessel health combine vitamin K with D3 and calcium for all-around vascular support.
Vitamin K has also been noted as a great aid for spider veins.
5. Bioflavonoids: Enhancing Circulation and Vein Health
Bioflavonoids, while not technically vitamins, are plant compounds that offer various benefits for vein health.
- Blood Thinning: Bioflavonoids have mild blood-thinning effects, which can improve circulation.
- Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties: They also possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, reducing stress on the veins.
Studies have shown that bioflavonoid supplementation can improve circulation and reduce symptoms in individuals with circulatory problems [7].
Traditional botanicals like Ginkgo + Ginseng for blood flow also support nitric oxide production and microcirculation.
Nourish Your Veins with Vitamins
Vitamins for varicose veins offer a natural and effective way to support vein health, improve circulation, and potentially reduce the appearance of these unsightly veins. Incorporate these vitamins into your diet or consider supplementation to give your veins the nourishment they need.
If you’re looking for more information, check out our article on the best vitamins for blood circulation.
FAQ
Not by themselves. Vitamins can support vein integrity, circulation, and symptoms (aching, heaviness), but only medical procedures remove existing varicose veins. Think “supportive care,” not “erasure.”
B3 (Niacin): supports circulation and nitric-oxide signaling.
B6 & B12: help manage homocysteine, easing vascular stress.
Vitamin C: needed for collagen & elastin (stronger vein walls) and supports nitric oxide.
Vitamin E: antioxidant that helps keep platelets from clumping.
Vitamin K: supports vessel integrity in tiny capillaries.
Bioflavonoids (e.g., diosmin/hesperidin/rutin): plant antioxidants that aid microcirculation and swelling.
If you’re consistent, expect 6–12 weeks for subtle changes in leg comfort or appearance. Pair nutrients with movement (walking, calf raises), leg elevation, weight management, and—if advised—compression.
Yes—check with your clinician if you:
take blood thinners (vitamin E may increase bleeding risk; vitamin K can affect warfarin dosing),
have liver or glucose issues (high-dose niacin isn’t for everyone),
are pregnant/breastfeeding, or planning surgery,
are considering very high doses of any vitamin (stick to sensible amounts unless supervised).
They may soften color/bruise look and skin tone, but they won’t shrink true varicose veins. For cosmetic removal, sclerotherapy or laser is the route—topicals are complementary.
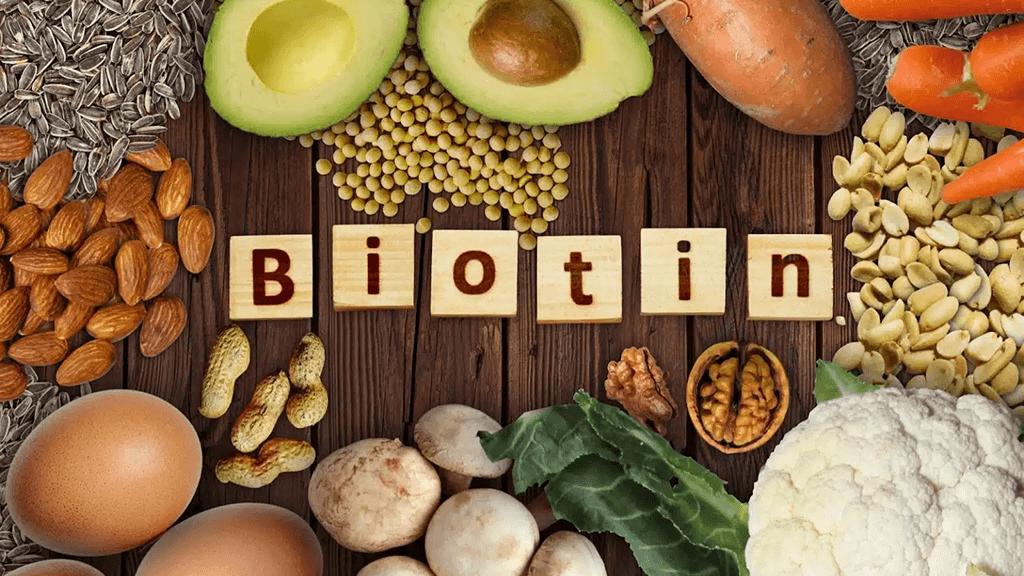
Yep:
C: citrus, peppers, berries
E: almonds, sunflower seeds, avocado
K: leafy greens (spinach, kale)
B3/B6/B12: fish, poultry, eggs, dairy (or fortified options)
Bioflavonoids: citrus peel, buckwheat (rutin), berries
Cites and Sources
No Citations
Show Citations
[1] - Zhang, Z., Liu, M., Zhou, C., He, P., Zhang, Y., Li, H., Li, Q., Liu, C., & Qin, X. (2021). Evaluation of dietary niacin and New-Onset hypertension among Chinese adults. JAMA Network Open, 4(1), e2031669. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.31669
[2] - Dionisio, N., Jardin, I., Salido, G. M., & Rosado, J. A. (2010). Homocysteine, intracellular signaling and thrombotic disorders. Current Medicinal Chemistry, 17(27), 3109–3119. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710791959783
[3] - Garg, A., & Lee, J. C. (2022). Vitamin E: Where are we now in vascular diseases? Life, 12(2), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020310
[4] - Garg, A., & Lee, J. C. (2022b). Vitamin E: Where are we now in vascular diseases? Life, 12(2), 310. https://doi.org/10.3390/life12020310
[5] - May, J. M., & Harrison, F. E. (2013). Role of vitamin C in the function of the vascular endothelium. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling, 19(17), 2068–2083. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5205
[6] - Hariri, E., Kassis, N., Iskandar, J., Schurgers, L. J., Saad, A., Abdelfattah, O., Bansal, A., Isogai, T., Harb, S. C., & Kapadia, S. (2021). Vitamin K2—a neglected player in cardiovascular health: a narrative review. Open Heart, 8(2), e001715. https://doi.org/10.1136/openhrt-2021-001715
[7] - Cesarone, M. R., Belcaro, G., Agus, G. B., Ippolito, E., Dugall, M., Hosoi, M., Corsi, M., Cotellese, R., Feragalli, B., Scipione, C., Scipione, V., & Maione, C. (2019). Chronic venous insufficiency and venous microangiopathy: management with compression and Pycnogenol®. Minerva Cardioangiologica, 67(4). https://doi.org/10.23736/s0026-4725.19.04948-x